Origins of Ancient Dice: From Divination Tools to Gambling

Dice are commonly known as small objects that are used for playing various games in social settings. Dice are traditionally shaped as cubes where each side of the dice is marked by small dots (from one to six). The dots are placed in specific patterns that are meant to add up to seven. These days, dice are primarily used to produce a random outcome of numbers during a gambling session. The standard design of a pair of dice may vary depending on the game that is played.
Standard LED-powered dice

Most games that involve dice require the players to throw the dice, roll the dice, flip them, shot them, or toss them. Dice can also be cast by the player in charge or tossed by means of a tool known as the dice cup. Dice cups are designed in a way that the dice will be flipped at random. The numbers that you see when the dice have been tossed are the ones that decide the outcome of the game. For instance, the player may win, lose, or add more points to their personal score depending on the type of game they are playing.
The ancient equivalent of modern dice was first mentioned by Sophocles, who insisted that the dice have been known to the Greeks since the legendary siege of Troy. The ancient historian Herodotus was certain that the dice had been famously popular among the people of Lydia back in the days of King Atys. However, the statements of the renowned chroniclers were soon debunked by the archeological discoveries suggesting that dice appeared way before the ancient Greeks roamed the Earth. The prototypes of dice were magical cubes that were believed to divine future events.
The prototypes of dice
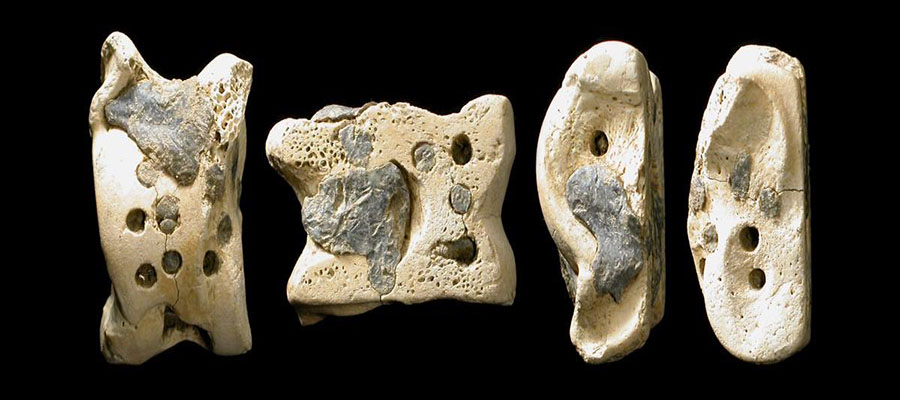
These mystical items included the anklebones of some of the domestic animals like sheep and are still actively used in rituals across the world.
Ancient Roman and Greek Dice: Chance and Mathematical Probability
Greeks and Romans made it a custom to manufacture dice from ivory and bone. Some of the dice that can be found at archaeological sites clearly indicate the presence of crystals, rock, marble, amber, and porcelain among the manufacturing materials. The scientific community was left in awe after the digs from 600 BCE in the Eastern Chinese region revealed the presence of cubical dice, among other artifacts. The earlier mentions of dice can be found in the traditional Indian epos like Mahabharata, with entertaining tales of dice-gambling sessions written in Sanskrit.
Pyramidal dice are duly considered just as ancient as classic cubical dice. They were used in the Royal Game of Ur, one of the most detailed and extensive board games ever known to humanity. The first indications that led to the discovery of the Royal Game of Ur can be found in Sumer texts that date back to the third millennium.
An example of pyramidal dice

However, gaming was not the only reason dice were madly popular among the common folk and royals back in the day. Numerous historical facts confirm that ancient civilizations such as Egyptians used cubical dice to divine the future of the country and the fates of the world. Excavations in and around Egyptian tombs prove that the appearance of dice can be documented as early as 2000 BC. Some of the researchers agree that the indigenous people of America could also use dice because of their magical properties. With markings on all four sides, these objects were rumored to help the augurs see beyond the mists of the unknown.
Cubical dice as we know them now first originated in China. Although there is no consensus among the historians as to how the game of dice made its way to the European courts of old, many suggest that the dice were probably brought to Europe after one of Marco Polo’s journeys that occurred during the fourteen century.
Ancient copper dice set, a modern reimagining

Dice were mostly made by hand and produced in relatively small quantities. This went on until the beginning of the twentieth century. When the innovative technology was invented, along with the introduction of plastic materials to the large corporations, dice production escalated immensely. By then, the players were thoroughly convinced that the falling of dice could be attributed to mathematical probability rather than sheer luck or supernatural forces. In ancient times, it was a common belief that the random combination of numbers that define the outcome of the game could be explained with the help of supernatural phenomena. Philosophers and thinkers of Ancient Greece were certain that it was the hand of the gods that determined the course of the game.
Dice, with their six sides and markings that changed depending on the culture the players came from, are the traditional epitome of fortune and fate. This was the predominant attitude of the ancient Romans many centuries ago. According to historians, most Romans considered any favorable change in the gambling succession to be a sign of the God’s benevolence and goodwill. Some archaeologists confirm that the successful rolling of the dice was an equivalent of luck and the felicitous disposition of the city’s deities.
High rolls were never taken for granted: they were a symbol of the God’s patronage and eternal protection. Rolling three sixes was associated with the benevolence of Venus, who seemed to take special pleasure in watching the players try their luck. Ellen Swift, who has been studying Roman habits of tying fortune with the divine, says that dice were an essential part of the Roman mentality, having a connection with the spiritual and serving as an antidote for non-believers. It was noticed that earlier dice did not have a cubical shape that is now considered standard across the world. Some of them were longer, while others did not match the description of a perfect gaming set that was found in China in 600 BC. Based on Swift’s studies, this can be related to the Roman way of thinking about the material world. The shape and the configuration of dice were not of utmost importance: other forces were in charge when it came to predicting the game’s twists and turns.
Modern Dice and Social Games: Changing the Course of History
Today, all dice are manufactured in the same way: they are produced from cellulose and plastic. This does little for the imagination of the archivists writing about implements made of bone and ivory. There are two types of dice you can come across while gambling on a regular basis: perfect and imperfect dice. Perfect dice belong to the realm of casinos. These dice are made with sharp edges. They are handcrafted for professional gambling such as craps and can be easily detected among the selection of imperfect dice, also known as round-cornered dice. Imperfect dice are usually made with the help of machines and are produced for social gatherings and different types of board games.
Round-cornered dice

The earliest physical proof of the existence of ancient dice was found at the site in Turkey. The dice that have been excavated in the process date back to the Bronze Age. This is sufficient confirmation for skeptics who claim that ancient civilizations were not interested in board games as fiercely as their descendants. History suggests that due to the fascination of Romans with the game of dice, specific laws were issued to prevent people from gambling in the nighttime hours. The most treasured dice with 20 sides were discovered in the Egyptian region. These dice are made of Serpentine and were used for ancient gambling sessions by our ancestors.
Perfect dice are famous for their conventional shape and form. They are usually referred to as level dice. Round-cornered dice, on the contrary, are also known as board dice. There are also crooked dice used for cheating during the game. These dice have been found in some of the Asian regions and North America, their forms varying based on geographical location.
Any type of dice that does not correspond to the classic shape of a perfect cube removes the possibility of mathematical odds. It can be tossed without considering arithmetic probabilities. For instance, flat dice will most likely land on larger surfaces. If the sides of the dice have been cut or trimmed, it will roll off accordingly. Shapes are the most popular types of dice when it comes to crooked dice. Due to the increasing amount of occurrences that involve crooked dice, casinos have implemented a system that involves tables with slanted walls. If the dice are tossed, they will be rebound from the walls to minimize the risk of cheating and provide the safety of the players. The history of dice, dating back to the third millennium, can help us understand the importance of gambling with perfect shapes.